Introduction
Root Cause Analysis is a structured approach to identifying and addressing the underlying causes of problems or issues within an organization.
It helps in identifying the underlying reason behind a problem rather than just fixing the symptoms.
Basics steps to follow for any Root Cause Analysis:
- Define the problem: Clearly define the problem or issue that needs to be addressed.
- Gather data: Collect relevant data and information related to the problem.
- Analyze the data: Analyze the data to identify potential causes of the problem.
- Identify the root cause: Identify the underlying cause of the problem.
- Develop a plan: Develop a plan to address the root cause of the problem.
- Implement the plan: Implement the plan to address the root cause of the problem.
- Monitor and evaluate: Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the plan in addressing the root caus
- Take corrective action: Take corrective action if the plan is not effective in addressing the root
- Document the results: Document the results of the Root Cause Analysis and the corrective actions tak
- Review and revise: Review and revise the Root Cause Analysis process as needed.
- Communicate the results: Communicate the results of the Root Cause Analysis to relevant stakeholders
- Follow up: Follow up on the corrective actions taken to ensure that they are effective in
- Continuously improve: Continuously improve the Root Cause Analysis process to ensure that it is
- Document lessons learned: Document lessons learned from the Root Cause Analysis process to
- Share knowledge: Share knowledge and best practices from the Root Cause Analysis process with
- Continuously monitor: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the corrective actions taken
🔹 The Four Buckets Framework for RCA
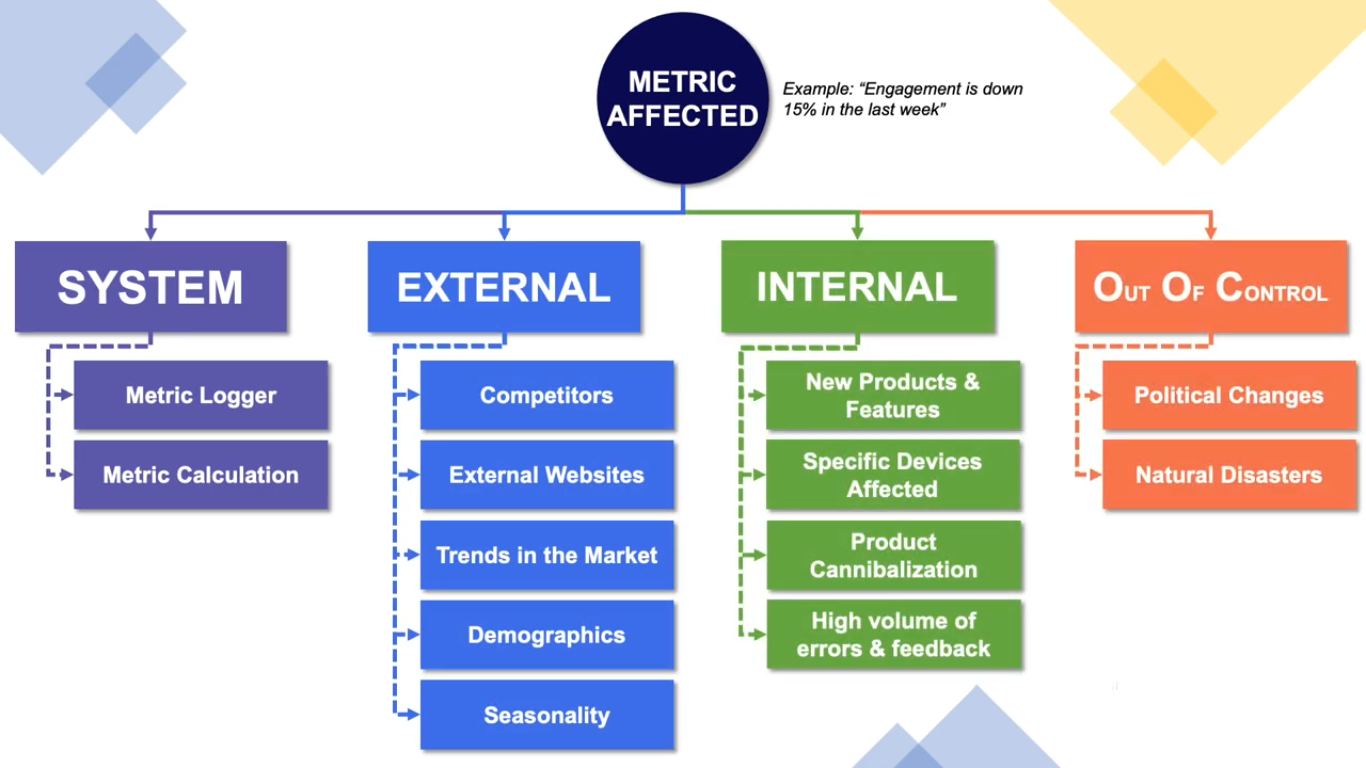
This framework categorizes potential causes of a metric drop into four main areas:
1️⃣ System Issues (Measurement Errors)
- Problems with data logging, metric calculation, or tracking.Example: Google Analytics is not capturing events correctly.
- Confirm metric calculations (e.g., MAU drop due to inactive users being counted incorrectly).
2️⃣ External Factors (Market & Competitive Landscape)
- Competitor moves, external website changes, market trends, seasonality, or demographics.
- Example: A competitor launches a heavy discount campaign.
3️⃣ Internal Factors (Product & Feature Changes)
- New feature releases, device-specific issues, product cannibalization, or high bug reports.
- Example: A redesign led to lower conversion rates.
4️⃣ Out of Control Events (Uncontrollable External Forces)
- Political changes, natural disasters, regulatory issues.
- Example: A government ban on certain types of ads.
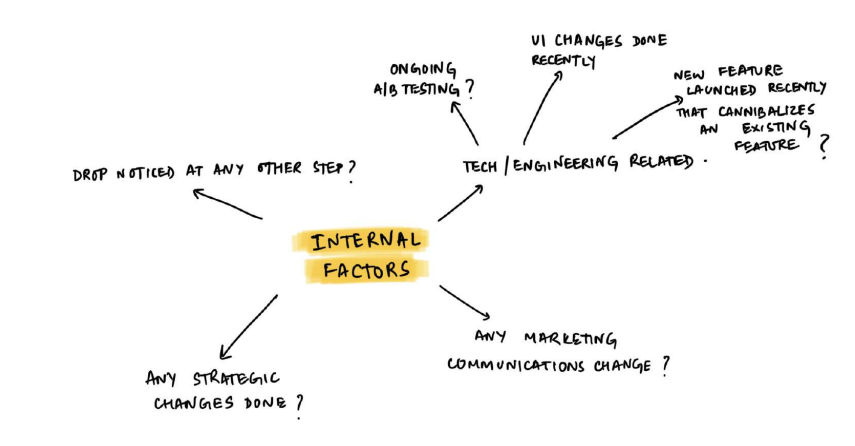
1. Internal factors
2. External factors

Example
Refs
← Previous postBasics of Incident Management
Next post →Top Prioritization Framework-1
